The body doesn't function properly without essential nutrients. Nutrients fuel bodily processes and maintain overall health.
Proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining bodily functions and overall well-being. Nutrients like vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates play specific roles in the body.
They support immune function, energy production, and cellular repair. Without adequate nutrients, the body struggles to perform these vital tasks efficiently.
This can lead to weakened immunity, fatigue, and various health issues. Consuming a balanced diet ensures the body receives the necessary nutrients to thrive.
It is important to understand the significance of a nutrient-rich diet for maintaining optimal health and preventing deficiencies. Prioritizing proper nutrition is key to sustaining energy levels and promoting long-term well-being.
Credit: www.quora.com
Introduction To Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies occur when the body lacks essential nutrients. These nutrients are vital for proper bodily functions. Without them, the body cannot work as it should.
Nutritional deficiencies can lead to many health problems. Understanding these deficiencies is key to maintaining good health.
The Role Of Nutrients In The Body
Nutrients are the building blocks of our bodies. They are essential for growth, energy, and repair. The body needs a balanced diet to get these nutrients.
- Vitamins: Help in various bodily functions.
- Minerals: Support bone health and fluid balance.
- Proteins: Build and repair tissues.
- Carbohydrates: Provide energy.
- Fats: Support cell growth and protect organs.
Consequences Of Inadequate Nutrition
Inadequate nutrition can lead to many health issues. Some consequences include:
- Weak Immune System: The body cannot fight off infections.
- Poor Growth: Children may not grow properly.
- Fatigue: Lack of energy and constant tiredness.
- Skin Problems: Dry, flaky skin and other issues.
- Bone Weakness: Increased risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
| Nutrient | Role | Deficiency Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | Produces red blood cells | Anemia |
| Vitamin D | Maintains bone health | Rickets |
| Calcium | Supports teeth and bones | Osteoporosis |
| Vitamin A | Maintains vision and skin health | Night blindness |
Macronutrients And Their Importance
The human body relies on macronutrients to function properly. These essential nutrients include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a unique role in maintaining health and energy levels.
Carbohydrates As Energy Sources
Carbohydrates are the body's main energy source. They break down into glucose, which fuels cells and brain function.
- Simple carbohydrates: quick energy, found in fruits and sugars.
- Complex carbohydrates: longer-lasting energy, found in grains and vegetables.
Without adequate carbohydrates, the body struggles to maintain energy and focus.
Proteins And Tissue Repair
Proteins are crucial for building and repairing tissues. They are made of amino acids, which are the building blocks of life.
- Animal proteins: found in meat, fish, and dairy.
- Plant proteins: found in beans, nuts, and seeds.
Proteins also support immune function and enzyme production. Lack of protein can lead to muscle weakness and poor recovery.
Fats And Cellular Function
Fats are essential for cellular function and energy storage. They help absorb vitamins and protect organs.
| Type of Fat | Source | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Unsaturated fats | Olive oil, avocados | Heart health |
| Saturated fats | Butter, red meat | Energy storage |
| Trans fats | Processed foods | Avoid for health |
Without healthy fats, the body can't function properly. It may lead to vitamin deficiencies and poor brain function.
Micronutrients: Vitamins And Minerals
Micronutrients, including vitamins and minerals, are crucial for body functions. They support growth, disease prevention, and well-being. Without enough micronutrients, the body can't function properly. Let's explore why vitamins and minerals are essential.
Vital Vitamins For Bodily Functions
Vitamins are organic compounds necessary for various body functions. Here are some vital vitamins:
- Vitamin A: Supports vision, skin health, and immune function.
- Vitamin C: Aids in collagen production and boosts the immune system.
- Vitamin D: Helps in calcium absorption for strong bones.
- Vitamin E: Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
- Vitamin K: Essential for blood clotting and bone health.
Essential Minerals For Health
Minerals are inorganic elements that the body needs to function. Here are some essential minerals:
| Mineral | Function |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Builds strong bones and teeth. |
| Iron | Supports oxygen transport in the blood. |
| Magnesium | Regulates muscle and nerve function. |
| Potassium | Maintains fluid balance and muscle contractions. |
| Zinc | Boosts immune function and wound healing. |
Ensuring adequate intake of these vitamins and minerals is crucial. They help the body perform at its best.
Immune System Undernourishment
Immune system undernourishment is a significant issue that affects overall health. When the body lacks essential nutrients, the immune system weakens. This makes it harder to fight off infections and diseases. Ensuring proper nutrition is crucial for maintaining a strong immune system.
Compromised Disease Defense
Without adequate nutrients, the body's disease defense system becomes compromised. The immune system relies on a balanced diet to function effectively. Nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and proteins are essential for creating immune cells.
When the immune system is undernourished, it cannot produce enough white blood cells. This leads to a higher risk of infections and illnesses. Proper nutrition helps in maintaining the body's natural defense mechanisms.
Link Between Nutrition And Immunity
There is a strong link between nutrition and immunity. Vitamins A, C, and E, along with minerals like zinc and iron, play a crucial role. They help in the production and function of immune cells.
Here is a table that shows the importance of these nutrients:
| Nutrient | Role in Immunity |
|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Supports skin health and cell growth |
| Vitamin C | Boosts white blood cell production |
| Vitamin E | Protects cells from damage |
| Zinc | Helps immune cell function |
| Iron | Supports oxygen transport in blood |
Ensuring a diet rich in these nutrients is vital. It helps in keeping the immune system strong and functional. A balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is ideal.
Impact On Metabolic Processes
The body needs nutrients to function properly. Without these nutrients, the body cannot perform essential metabolic processes. Metabolism is crucial for energy production, cell repair, and overall health. Let's explore how nutrient deficiency affects metabolic processes.
Slowed Metabolism From Nutrient Deficiency
A lack of essential nutrients can slow down metabolism. The body needs vitamins and minerals to convert food into energy. Without these nutrients, this conversion process slows. This results in a slower metabolism.
Common symptoms of a slowed metabolism include fatigue and weight gain. The body struggles to burn calories efficiently. This can lead to increased fat storage and decreased energy levels.
Here are some key nutrients and their impact on metabolism:
| Nutrient | Role in Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Vitamin B | Helps convert food into energy |
| Iron | Supports oxygen transport in the blood |
| Magnesium | Involved in over 300 metabolic reactions |
Nutrients And Their Role In Metabolism
Nutrients play a vital role in metabolism. Each nutrient has a specific function. For instance, Vitamin B helps convert carbohydrates into glucose. This glucose is then used for energy.
Iron is another crucial nutrient. It supports the transport of oxygen in the blood. Without enough iron, cells cannot get the oxygen they need. This hampers the body's ability to produce energy.
Magnesium is involved in over 300 metabolic reactions. It helps with muscle function, nerve function, and protein synthesis. A deficiency in magnesium can disrupt these processes.
Here is a quick overview of some essential nutrients and their metabolic roles:
- Vitamin B: Energy production
- Iron: Oxygen transport
- Magnesium: Muscle and nerve function
- Zinc: Immune function
- Calcium: Bone health
Ensuring a balanced diet rich in these nutrients is key. A balanced diet supports optimal metabolic processes. It helps maintain energy levels, supports cell repair, and promotes overall health.

Credit: www.self.com
Cognitive Functions At Risk
The body requires essential nutrients to function properly. Without these nutrients, cognitive functions are at risk. This section explores how nutrient deficiencies affect brain health and mental performance.
Brain Health And Nutrients
The brain needs various nutrients to stay healthy. These include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, seeds, and nuts. They support brain cell structure.
- Vitamin B12: Present in meat, eggs, and dairy. It helps in nerve function and red blood cell formation.
- Iron: Found in spinach, lentils, and red meat. It aids in oxygen transport to the brain.
- Antioxidants: Found in berries, nuts, and vegetables. They protect brain cells from damage.
Effects Of Deficiencies On Mental Performance
Lack of essential nutrients can affect mental performance. Here are some effects:
| Deficiency | Effect on Mental Performance |
|---|---|
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Memory problems and mood swings |
| Vitamin B12 | Confusion and poor concentration |
| Iron | Fatigue and reduced cognitive function |
| Antioxidants | Brain cell damage and cognitive decline |
Maintaining a balanced diet ensures the brain gets necessary nutrients. This helps in preserving cognitive functions and mental performance.
Physical Symptoms Of Poor Nutrition
Poor nutrition can severely affect the body's overall health. Without the right nutrients, the body cannot function properly. This leads to various physical symptoms and long-term health issues.
Visible Signs Of Nutrient Deficiencies
Several physical signs can indicate nutrient deficiencies. Some of these visible signs include:
- Hair loss: Lack of protein and vitamins can cause hair to fall out.
- Dry skin: Vitamin A and C deficiencies can make skin dry and scaly.
- Brittle nails: Insufficient biotin and calcium can lead to weak nails.
- Pale skin: Low iron levels may result in a pale complexion.
- Bleeding gums: Vitamin C deficiency can cause gums to bleed easily.
Long-term Physical Consequences
Poor nutrition doesn't just show immediate signs. It can also lead to long-term physical consequences. Some of these include:
- Weakened immune system: Without proper nutrients, the immune system can't fight infections well.
- Bone disorders: Calcium and vitamin D deficiencies can lead to osteoporosis.
- Heart disease: Poor diet can increase the risk of heart-related issues.
- Type 2 diabetes: Unhealthy eating habits can lead to insulin resistance.
- Obesity: Lack of balanced nutrition can cause excessive weight gain.
| Deficiency | Visible Sign | Long-term Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | Pale skin | Anemia |
| Vitamin D | Weak bones | Osteoporosis |
| Vitamin C | Bleeding gums | Scurvy |
| Protein | Hair loss | Muscle wasting |
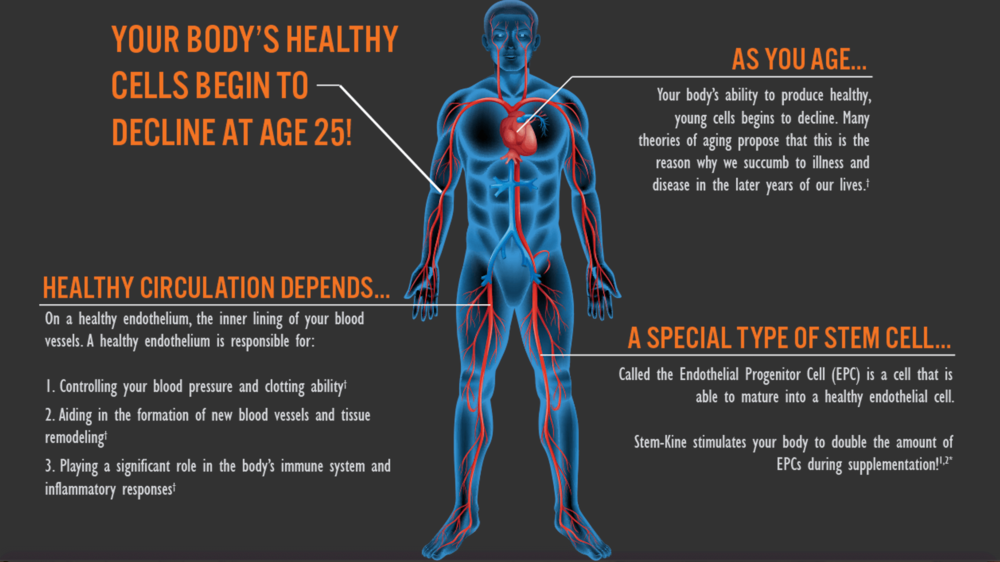
Credit: www.nychealthynutrition.com
Preventing Nutritional Deficiencies
Our bodies need essential nutrients to function properly. Without these nutrients, the body can't operate well. Nutritional deficiencies can cause health problems. They can make us feel tired, weak, and sick.
Balanced Diets And Supplementation
A balanced diet is crucial for health. It includes various foods from all food groups. This ensures we get a range of nutrients.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Whole Grains: Offer essential carbohydrates and fiber.
- Proteins: Found in meat, beans, and nuts. They help in growth and repair.
- Dairy: Supplies calcium and vitamin D for strong bones.
Sometimes, diet alone isn't enough. Supplements can help fill the gaps. It's important to choose the right ones. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements.
Recognizing And Addressing Dietary Gaps
Identifying nutritional gaps is key. It helps in preventing deficiencies. Common signs of deficiencies include:
- Fatigue
- Poor concentration
- Weak muscles
- Dry skin
Addressing these gaps involves checking your diet. Ensure you consume a variety of foods. Here is a simple table to help you understand daily nutrient requirements:
| Nutrient | Daily Requirement | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | 75-90 mg | Oranges, strawberries, bell peppers |
| Iron | 8-18 mg | Red meat, spinach, lentils |
| Calcium | 1000 mg | Milk, cheese, yogurt |
Eating a variety of foods helps meet these needs. If gaps remain, consider supplements. Always talk to a healthcare professional.
Case Studies
Understanding why the body doesn't function properly without nutrients is crucial. Real-life case studies offer valuable insights. This section focuses on individuals overcoming deficiencies and public health strategies on nutrition.
Individuals Overcoming Deficiencies
Many people experience health issues due to nutrient deficiencies. Let's explore a few cases:
| Name | Deficiency | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| John | Vitamin D | Fatigue, bone pain | Supplements, sunlight |
| Sarah | Iron | Weakness, dizziness | Iron-rich diet, supplements |
| Mike | Vitamin B12 | Numbness, memory issues | B12 injections, diet change |
Public Health Strategies On Nutrition
Public health strategies help communities get proper nutrients. Here are some effective strategies:
- Fortified foods: Adding vitamins and minerals to foods.
- Education programs: Teaching about balanced diets.
- Supplement distribution: Providing vitamins to at-risk groups.
- School meal plans: Ensuring kids get nutritious meals.
These strategies show how public health can address nutrient deficiencies. They improve health on a larger scale. Ensuring everyone gets the nutrients they need is essential for a healthy society.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why Are Nutrients Essential For The Body?
Nutrients are essential because they provide the energy and support the body needs to function properly. They help in growth, repair, and maintaining overall health.
What Happens If The Body Lacks Nutrients?
If the body lacks nutrients, it can't perform necessary functions. This can lead to weakness, poor immunity, and various health issues.
How Do Nutrients Affect Bodily Functions?
Nutrients affect bodily functions by supporting metabolic processes, energy production, and cell repair. They are crucial for maintaining overall health and vitality.
Can Nutrient Deficiency Cause Long-term Health Problems?
Yes, nutrient deficiency can cause long-term health problems. It can lead to chronic diseases, poor mental health, and reduced quality of life.
Conclusion
A lack of essential nutrients disrupts the body's normal functions. It leads to fatigue, weakened immunity, and poor health. Nutrient-rich diets are crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
Prioritize balanced meals to ensure your body gets what it needs. Proper nutrition is key to a healthy, functioning body.
